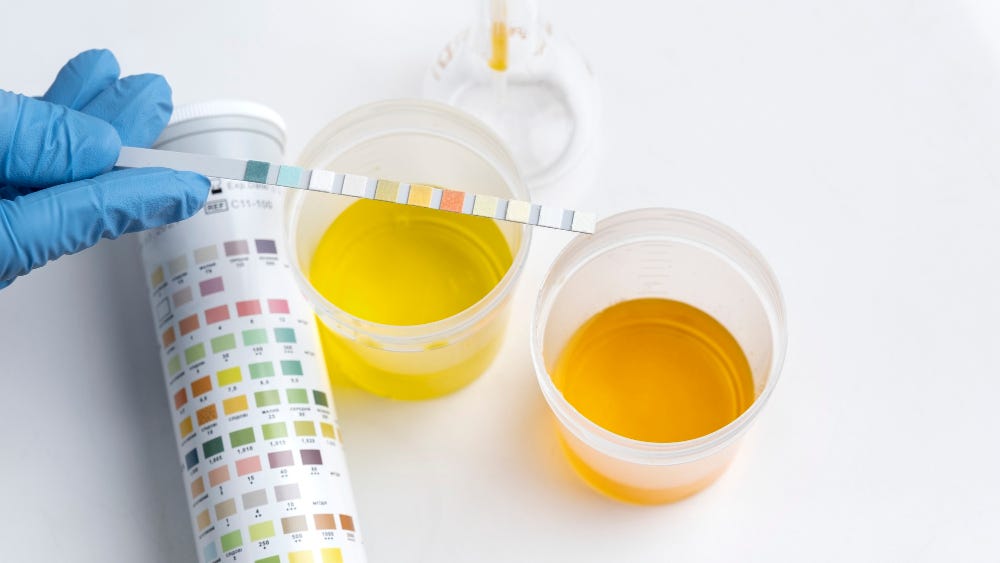
Pus cells in urine, a common concern for many, can indicate an underlying health issue. Pus cells are a bunch of dead white blood cells that gather where there’s an infection. When these pus cells show up in your pee, it’s called Pyuria. Having a few pus cells in your pee is fine, but if there are too many, it might mean you have an infection. In this article, we’ll look closely at pus cells, what they are, why they end up in urine, what signs to watch out for, the usual range of pus cells in pee, and whether it’s normal to find them there. Let’s will delve into the normal range of pus cells in urine and explore treatment options. If you suspect a problem, we’ll also guide you to the best diagnostic centre in Kolkata & Bhopal, including the top pathology lab in the city.
Understanding Pus Cells: What Are They?
Pus cells are a bunch of dead white blood cells that gather when your body fights off an infection. They create a yellowish fluid called liquor puris at the infection site. Sometimes, you might find these pus cells in your urine. This is called pyuria.
Pyuria: Types and Causes
Pyuria comes in two types: sterile and non-sterile. Sterile pyuria means pus cells in urine without any bacteria. Non-sterile pyuria is when bacteria are present along with pus cells.
What is the Normal Range of Pus Cells in Urine?
People often wonder if it’s normal to find pus cells in their urine during routine tests or when they have urinary issues. While a few pus cells are okay, having a lot of them is not.
It’s usual to have a few pus cells in your urine. The normal count can vary a bit for men and women. For men, it’s less than 4 cells per high-power field (HPF), while for women, it’s around 5 to 7 cells per HPF.
If you see changes in your urine like it getting thick or cloudy like pus, it’s a sign something might be up, and you should talk to a doctor.
It might mean you have a urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney problems, or other health concerns. Regular urine tests from a top pathology lab in the city and seeing a doctor can catch and treat these issues, keeping your urinary health and overall well-being in check.
When Should You Get a Pus Cell Urine Test?
If you notice any of these signs, it’s a good idea to get a urine test:
- Cloudy urine: If your pee looks cloudy, it might have pus cells.
- Changes in pee: Any weird changes in how your urine looks or feels.
- Peeing more often: If you’re running to the bathroom more than usual.
- Blood in urine: If your pee has blood in it, that’s a red flag.
- Pain when peeing: A burning feeling when you go.
- Pelvic pain: Discomfort in your lower belly.
- Smelly urine: If your pee has a foul odor.
- Fever: If you’re running a temperature.
- Abdominal pain: Pain in your tummy.
- Shortness of breath: Having trouble breathing.
- Vaginal discharge: Unusual stuff coming from there.
- Vomiting or feeling sick: Throwing up or feeling queasy.
Diagnosing Pyuria: How It’s Done
To figure out if you have pyuria, your doctor will suggest a urine test, which is a standard way to check for different issues. Here’s how it works:
Step 1: Collecting Urine Sample
First, you provide a pee sample. Usually, it’s the middle part of your pee after cleaning the private area with an antiseptic.
Step 2: Microscopic Check
Next, they look at your pee under a microscope to see if there are pus cells. Normally, there are very few or none. But if you have an infection or inflammation, there will be more pus cells.
Step 3: Counting Pus Cells
They count how many pus cells they find and report it as the number of cells in a small part of the microscope.
Step 4: Culture and Sensitivity Test
If they see lots of pus cells, they might do another test. This one help find the specific bacteria causing the infection and the best medicine to treat it.
So, the best medicine for pus cells in urine depends on the results of these tests.
Having pus cells in your urine is an important sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI). Don’t ignore it. If you feel a burning sensation or need to pee more often, get a urine test right away. Understanding the normal range of pus cells in urine and seeking timely treatment when needed is essential for maintaining good health. Remember that early detection and proper management of underlying causes can prevent complications. When in doubt, trust the experts at Health Care Diagnostic Clinic & Laboratory Services, the best diagnostic center in Kolkata & Bhopal, to provide you with accurate diagnostic services and guide you toward better health.