The Cardiological Society of India (CSI) has introduced the nation’s inaugural guidelines for managing dyslipidemia, a condition characterized by abnormal lipid levels in the blood, which is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. These guidelines are tailored to the Indian population, leveraging extensive local data to provide relevant and effective management strategies.
The Importance of the Guidelines
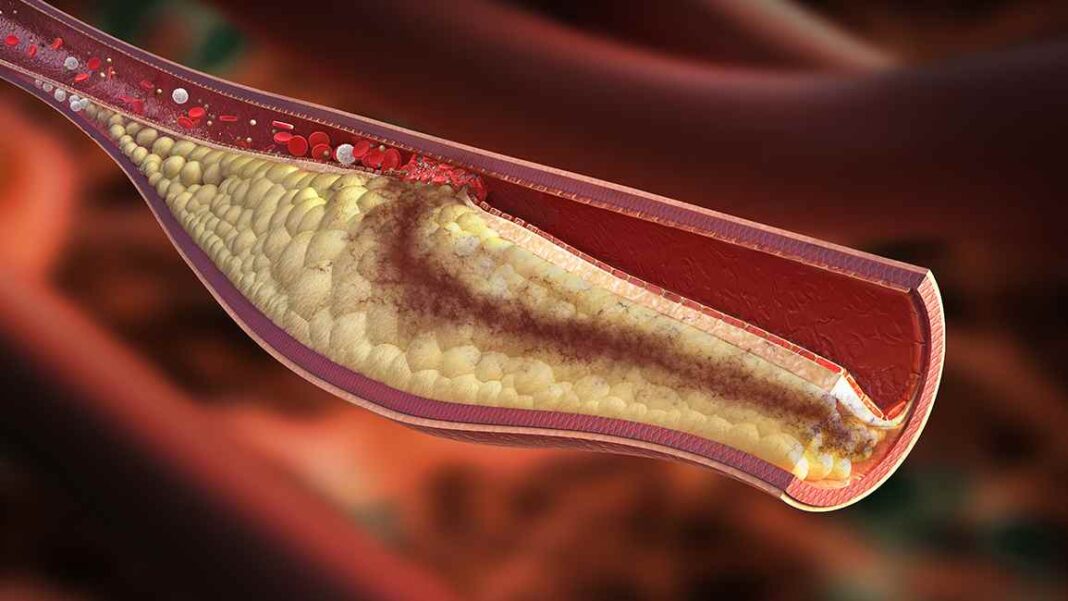
Dyslipidemia is a critical public health issue in India, contributing significantly to the burden of cardiovascular diseases. The newly released guidelines by CSI are a comprehensive effort to address this problem by providing healthcare professionals with clear, evidence-based protocols for diagnosing and managing dyslipidemia. This initiative aims to standardize care, improve patient outcomes, and reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events related to abnormal lipid levels.
Key Recommendations
- Non-Fasting Lipid Measurements: The guidelines recommend the use of non-fasting lipid profiles for risk assessment and treatment decisions. This approach simplifies the testing process and encourages more individuals to get screened, as it removes the need for fasting before blood tests.
- LDL-C and Non-HDL Cholesterol Targets: New target levels for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) have been established, stratified according to different risk categories. These targets are critical for tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Emphasizing the role of lifestyle changes, the guidelines advocate for dietary modifications, increased physical activity, and weight management as first-line interventions for managing dyslipidemia. These non-pharmacological measures are crucial for improving lipid profiles and overall cardiovascular health.
- Pharmacotherapy: For patients who do not achieve lipid targets through lifestyle changes alone, the guidelines recommend the use of statins as the primary pharmacological treatment. Additionally, newer lipid-lowering therapies, such as PCSK9 inhibitors and ezetimibe, are suggested for high-risk patients or those with statin intolerance.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of lipid levels and cardiovascular risk factors is encouraged to ensure that treatment goals are met and maintained. Regular follow-up appointments and lipid profile tests are essential components of effective dyslipidemia management.
Impact on Public Health
The introduction of these guidelines marks a significant advancement in the fight against cardiovascular diseases in India. By providing a structured approach to dyslipidemia management, CSI aims to enhance the quality of care delivered by healthcare professionals across the country. The guidelines are expected to facilitate early detection, prompt intervention, and consistent management of dyslipidemia, thereby reducing the prevalence of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
Role of Diagnostic Centres
Diagnostic centres in Kolkata like Health Care Diagnostic Clinic & Laboratory Services and other regions play a pivotal role in the implementation of these guidelines. These centres are equipped to perform the recommended lipid profile tests and provide accurate, timely results that are crucial for effective management. Collaboration between diagnostic centres and healthcare providers is essential to ensure that patients receive comprehensive care that aligns with the new guidelines.
Conclusion
The release of the first national guidelines for dyslipidemia management by the Cardiological Society of India is a landmark achievement in the realm of cardiovascular health. These guidelines provide a clear, evidence-based framework for the diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia, tailored to the unique needs of the Indian population. By adhering to these guidelines, healthcare professionals can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases in India.