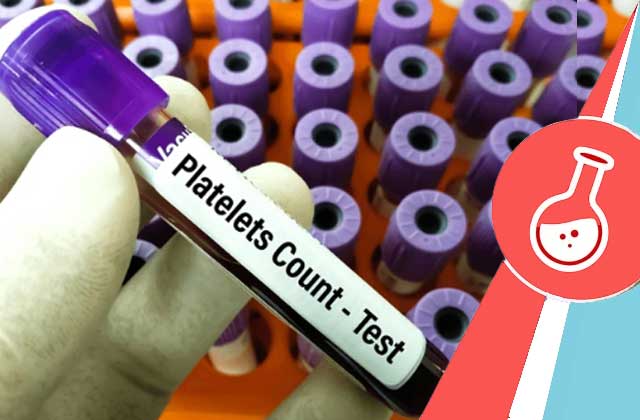
A platelets (PLT) blood test is an essential diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about your overall health, especially concerning your blood’s ability to clot. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are tiny blood cells that play a crucial role in stopping bleeding by forming clots. Understanding the PLT blood test, its normal range, and how to manage platelet count levels can significantly impact your health. In this blog, we will delve into the importance of the PLT blood test, the implications of having high or low platelet counts, and ways to increase platelet count naturally.
What is a PLT Blood Test?
A PLT blood test measures the number of platelets in your blood. This test is part of a complete blood count (CBC) and helps diagnose various health conditions, including clotting disorders, bleeding problems, and bone marrow diseases. It is commonly ordered during routine check-ups or when a patient shows symptoms of a blood disorder.
Importance of the PLT Blood Test
Platelets are critical for maintaining hemostasis, the process that prevents excessive bleeding when you have a wound. Without adequate platelets, even minor injuries could result in significant blood loss. Conversely, too many platelets can lead to abnormal clotting, which can cause conditions such as stroke or heart attack. Thus, maintaining a proper platelet count is vital for health.
PLT Blood Test Normal Range
The normal range for platelet count varies slightly between laboratories, but it typically falls between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Here’s a breakdown:
- Normal Range: 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter
- Mild Thrombocytopenia: 100,000 to 150,000 platelets per microliter
- Moderate Thrombocytopenia: 50,000 to 100,000 platelets per microliter
- Severe Thrombocytopenia: Less than 50,000 platelets per microliter
- Thrombocytosis: More than 450,000 platelets per microliter
High Platelet Count (Thrombocytosis)
A high platelet count, or thrombocytosis, can occur due to several reasons. It may be a reactive response to conditions such as infection, inflammation, iron deficiency, or after surgery. In some cases, it can be due to bone marrow disorders like essential thrombocythemia or polycythemia vera. Symptoms of high platelet count can include headaches, dizziness, chest pain, and weakness.
Causes of High Platelet Count:
- Inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis)
- Infections
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Cancer
- Splenectomy (removal of the spleen)
Managing High Platelet Count: If you have a high platelet count, it’s essential to consult with reputed diagnostic centre in Kolkata & Bhopal to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. In some cases, medications or procedures may be necessary to reduce the platelet count and prevent complications.
Low Platelet Count (Thrombocytopenia)
A low platelet count, or thrombocytopenia, can lead to increased bleeding and bruising. It can result from various conditions, including autoimmune diseases, viral infections (like dengue fever), certain medications, chronic liver disease, and bone marrow disorders.
Symptoms of Low Platelet Count:
- Easy or excessive bruising
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts
- Spontaneous bleeding from gums or nose
- Blood in urine or stools
- Fatigue
How to Increase Platelet Count
If you have a low platelet count, there are several natural ways to help increase it:
- Dietary Changes:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are rich in vitamin K, which is essential for blood clotting.
- Fruits: Papaya and pomegranate are known for boosting platelet production.
- Vegetables: Beetroot and carrots are beneficial for overall blood health.
- Supplements:
- Vitamin B-12 and Folate: These vitamins are crucial for platelet production. Foods rich in B-12 include eggs, dairy, and meat, while folate is abundant in leafy greens, beans, and citrus fruits.
- Iron: Iron-rich foods like red meat, lentils, and fortified cereals can help improve platelet count.
- Hydration:
- Drinking plenty of water helps maintain the fluidity of blood and supports overall cell function.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Certain Medications:
- Alcohol can decrease platelet count, so it’s best to avoid it if you have thrombocytopenia. Some medications, including aspirin and ibuprofen, can also affect platelet function.
- Rest and Reduce Stress:
- Adequate rest and stress management can positively impact your immune system and overall health, aiding in platelet production.
Conclusion
Understanding your platelet count through a PLT blood test is crucial for diagnosing and managing various health conditions. Whether you have a high or low platelet count, knowing the PLT blood test normal range helps you take the necessary steps to maintain or achieve a healthy platelet level. If you experience symptoms related to abnormal platelet counts, consult with your healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. By following a healthy diet and lifestyle, you can support your body in maintaining optimal platelet levels.
For more information on managing your platelet count or to schedule a PLT blood test at Health Care Diagnostic Clinic & Laboratory Services
Stay informed and proactive about your health!